As water flows naturally underground, it picks up variety of the minerals that are dissolved in the peripheral soil and rocks. These minerals typically embrace sulfates, that ar gift in just about every variety of water found in nature, yet as groundwater, ocean-water, and water, and even petroleum and brines. they’re to boot gift in many industrial wastes as a results of the facility’s process—mainly in mining and mineral dressing applications where sulfates area unit unearthed via minerals like salt (gypsum), sulphate (Epsom salt), and sulfate (Glauber’s salt). In high concentrations, sulfates could {also be |is also} harmful to human health and also the environment and corrosive to pipes and instrumentality, in order that they are one factor many industrial facilities look to induce obviate whether or not or not the intent is for unhitch into the native POTW or surroundings or apply at intervals the facility’s technique.
You might be questioning, what ar the foremost effective technologies for removing salt from your method and wastewater? Here, we tend to look at the assorted ways that used and whether or not or not or not your facility need to take under consideration the sulfate-removal techniqueology therefore you will build the foremost effective picks accomplishable for your method.
Removing sulfates with sorption
Adsorption harnesses the molecular forces of attraction to capture contaminants from a liquid stream. the strategy consists of passing a liquid stream through some variety of porous, adsorbent media, and once the soluble contaminants ar heaps of drawn to the adsorbent media than they are to the water at intervals the stream, the contaminants bind to the surface of the media whereas the liquid effluent flows through. sorption is effective for removing sulfates at relatively low concentration levels and will be achieved with technologies like granular carbon filtration. although the technology is typically economical, the media will most likely need to be changed out generally, which can add up in every value and time.
Removing sulfates with lime
Many facilities choose to deduct sulfates, notably with larger concentrations, by adding lime (Ca(OH)2), which may precipitate out the salt as mineral. this may be useful for facilities that even have large amounts of great metals in their waste as a results of the salt could also be precipitated out at a cation concentration below what the metals would need to precipitate out. many facilities will see degree eightieth reduction in salt with lime before they even need to begin worrying concerning the metals, which may minimize the toxicity of initial secondary wastes and sludge created at intervals the precipitation technique. Typically the first step utilized within the well-known economical salt Removal (or CESR) technique, which can be integrated into many stuff treatment trains. once the initial step is completed (reducing the sulfates with hydrous lime–induced precipitation), the CESR technique typically yield with a cation concentration adjustment double-geared toward metals removal and an additional sulfate-removal step with a cation concentration increase and a second lime addition and treatment of any secondary wastes. many facilities like treating sulfates with lime as a results of lime is relatively reasonable and readily offered. Reducing salt to lower levels could also be achieved throughout a sharpening step with element salts, which can be extra to precipitate atomic number 56 sulfate (has a extremely low solubility in water). element addition is used throughout a sharpening step as element salts ar relatively higher in value.
Removing sulfates with distillation
With distillation, the sulfate-saturated liquids ar heated to boiling, then the following vapor is cooled throughout a condenser, and conjointly the sublimate water is captured throughout a sterile instrumentality. where some separation processes deduct the contamination from the liquid stream, distillation removes the liquid from the contaminants, that ar left behind at intervals the still once the water has gasified away. Distillation is very effective at removing sulfates, but detain mind that for several industrial applications, distillation wants very important energy expenses for heating, circulation, and cooling, notably for the massive volumes of water needed to support production on degree industrial scale. Over the previous couple of decades, innovations like vapor compression and multiple result distillation setups have diode to larger energy efficiency, but they are still expensive to run comparative to totally different purification technologies.
Removing sulfates with electro coagulation
As an easy definition, electro coagulation can be a technique of purifying water with the practice of electricity. Once submerged, metal plates and electrical currents charge the peripheral contaminated water, the particles cling onto each other and fall from the contaminated water. generally utilized by itself, the technology may additionally be incorporated into a pre- or post treatment half (before reverse diffusion, for example) to attenuate the contamination removal wishes of your membranes or to shine water that has to be at a stronger purity. this may be useful to facilities eager to minimize the necessity for chemicals.
Removing sulfates with action
Ion exchange systems are used across a variety of industries for water softening, purification, and separation functions. whereas the chemistry of individual action reactions varies from one application to sequent, this can be a treatment technique whereby dissolved ions are replaced by totally different, heaps of fascinating, ions of a similar electrical charge. This reaction typically takes place in degree IX column or vessel where a technique or waste stream is undergone a specialized raisin that facilitates the exchange of ions. once it involves the right action system for removing sulfates, you’ll typically want to see a rosin system full of a combination of particle (to deduct Ca and magnesium) and anionic resins (to then deduct sulfates). This technique works best for sharpening and with a background stream that is low in numerous competitive salts.
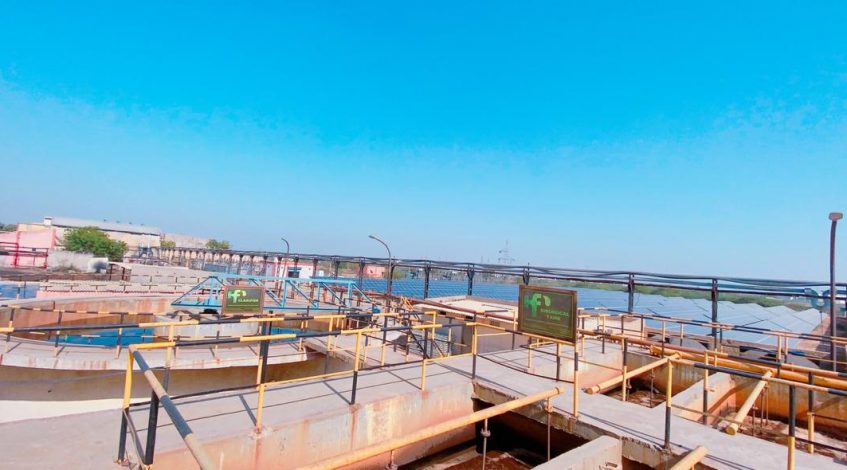
Removing sulfates with membrane filtration
Membrane filtration (like reverse diffusion (RO), nano-filtration (NF), and ultra-filtration (UF)), is one in each of the foremost effective technologies for removing sulfates from method and waste water. The technology can also be a cost-effective way to treat sweater and brine during the oil extraction process when the sulfates need to be removed efficiently to prevent system scaling and the creation of hydrogen sulfide, a harmful gas that can be created during the oil-extraction process when bacteria break down sulfates. Often used in combination with other technologies to lessen the membrane fouling outcomes and reduce the need for backwashing or membrane replacement, your facility might use a range of filters to gradually narrow down the particle size allowed through—for example, some facilities, depending on the sulfate concentration, might find it helpful to pre-treat their water and brine streams with UF before passing through a NF or RO unit.