Total dissolved solids or TDS now if I have a container of water that container of water then in that water let’s say just at the moment is pure water there is nothing there but water molecules okay if I add some salt to that to some sodium chloride that will dissolve if we add some sugar that river dissolve so we’ve got a sugar molecule there which is an organic carbohydrate right so a covalent molecular substance here we have an ionic compound sodium chloride if I was to add some ethanol that would dissolve okay and you know look you can see there can add a variety of things into this water so we have a concept called total dissolved solids and so in a water body.
Total dissolved solids (TDS) refers to the amount of minerals, metals, organic material and salts that ARE dissolved in a certain water volume that is expressed in mg/L. It is directly associated with the quality and purity of water, particularly in water purification systems.
Total dissolved solids may be suspended in forms such as:
• Molecular
• Ionized
• Micro-granular (colloidal sol)
we’re going to have lots of different compounds that are dissolved in the water that’s going to affect the water quality and after it rains we’re going to have a lot of these salts in fertilizers and salts in soil that will dissolve in the rain water and then leach into the waterway and therefore increase the amount of total dissolved solids in the water body all right so we’re going to work out how we can do that so this is first of all that total dissolved solids is the is all in a water sample so when we measure this of course you want to when you get your water supply want to filter it get rid of any in soluble solids once you get your filtrate then you know that we can go ahead and analyze any total dissolved solids in the water sample so in terms of numbers what have we got so if we have like a thousand parts-per-million that’s a lot of total dissolved solids and that means we have a degraded water supply so it’s contaminated with so much dissolved material that it makes it very hard or if not impossible for aquatic organisms and plants to survive another thing to watch out for in questions is if you have a high level of sodium ions then that’s going to indicate that there are so limited salinity problems if you have a high concentration of potassium ions that’s going to tell you have a lot of plant material that’s degrading in the water supply so that usually happens after large storms anyway where you get lots of organic leaves and branches and so forth in the water body.
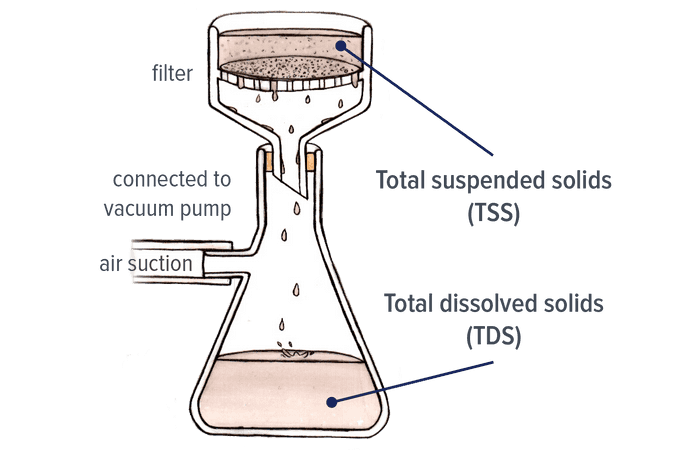
How to measure TDS ?
The two principal methods of measuring total dissolved solids are
• Gravimetric Analysis :- Gravimetric methods are the most accurate and involve evaporating the liquid solvent and measuring the mass of residues left. This method is generally the best, although it is time-consuming. If inorganic salts comprise the great majority of TDS, gravimetric methods are appropriate.
• Conductivity :- Electrical, or specific, conductivity of water is directly related to the concentration of dissolved ionized solids in the water. Ions from the dissolved solids in water create the ability for that water to conduct an electric current. which can be measured using a conventional conductivity meter or TDS meter.
Water Classification
Water can be classified by the level of total dissolved solids (TDS) in the water:
• Fresh Water : TDS is less than 1,000 ppm
• Brackish Water : TDS = 1,000 to 10,000 ppm
• saline Water : TDS = 10,000 to 35,000 ppm
• Hyper Saline : TDS greater than 35,000 ppm
Drinking water generally has a TDS below 500 ppm. Higher TDS Fresh Water is drinkable but taste may be objectionable.