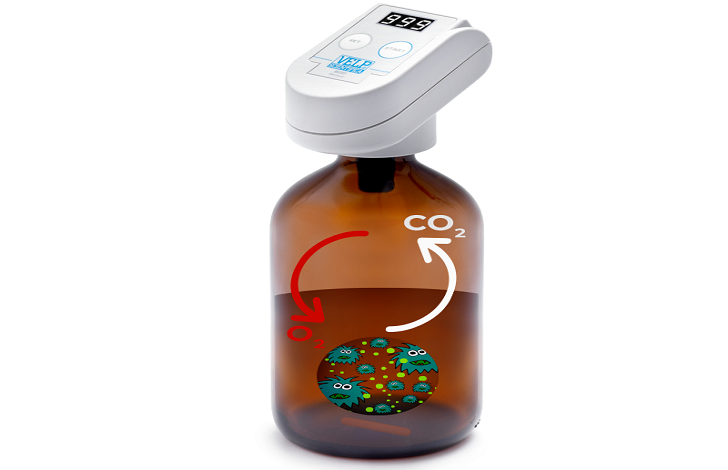
BOD – Biological oxygen demand is the most important used assessment to determine water quality.
It’s a measurement unit that stands for the needed amount of oxygen by aerobic biological organisms to break down organic matter. COD in comparison stands only for everything that can be chemically oxidized and is therefore less specific. The biochemical process of BOD removal can be described with the equation organic matter + O2 is converted into CO2 + H2O.
The biological oxygen demand, represents the quantity of oxygen required to stabilize, through biochemical processes. When organic matters such as, aquatic plants and animals dies, microorganisms get to work breaking them down under anaerobic conditions. In the presence of free oxygen, aerobic bacteria use the organic matter found in wastewater as “food”. The more “food” present in the waste water
As higher the degree of water pollution as more organic matter is present and as more oxygen is needed for the Oxidization, hence as higher is the BOD level. The most common laboratory test method used is called the BOD5 test. For this testing method one liter of wastewater is filled into a testing bottle and the consumed oxygen during five days of incubation is measured.
The test method uses five days of incubation time as after five days most organic material has already been degraded. The test sample is continuously agitated under the absence of light and a sensor measures the decline of pressure caused by oxygen consumption. Typical values for BOD levels are 2 to eight mg/l in moderately polluted rivers. In comparison untreated sewage in the US has a BOD level of about 300 milligrams per liter. Whereas European sewage averages around 600 milligrams per liter. The lower BOD level in the US is caused by a greater water use per capita. Wastewater treatment plants use different technologies to increase BOD removal significantly. One common method is to increase the amount of biological organisms by providing more surface area for attached growth. Film media plastic blocks consist of corrugated sheets and ensure a good water and air mixing to supply the biological organisms with nutrients and oxygen.
Each film media block can provide up to 250 m2 surface area for attached growth.
What is Ultimate biological oxygen demand?

The “Ultimate biological oxygen demand” is the amount of oxygen required to decompose all of the organic material after infinite time.
Advantages
Most closely models the natural environment when used with the proper ” seed “
Disadvantages
• Toxic materials kill microorganism
• Microorganism do not oxidize all materials present in waste
• Inaccuracies when used with improper “seed”
• Biological oxygen demand test measures only biodegradable organics.
• It takes five days to perform and uses a discrete sample.
• Pre-treatment is needed if the sample contains toxic wastes.
• It is essential to have high concentration of active bacteria present in the sample.
• The test has poor reproducibility and toxic chemicals can inhibit measurement.
What is Seed?
The term “seed” refers to microorganisms that consume the biodegradable organic matter in samples for biological oxygen demand measurement.